Table of Contents
Nearly every facet of today's world depends on a type of network to function. Computer networks are the backbone of every organization. But to the not-so-tech-inclined, it is a far too technical area they would rather leave to the tech support guys. While the techies' livelihood depends on fixing your system, it doesn't hurt to be conversant in an area much of our work depends on.
This article aims to introduce you to the fundamental concepts of networking. It doesn't assume any previous knowledge on your part and is intended to make you conversant with the most important concepts of networking.
What is Networking
Networking simply means the design and use of computer networks. A network is an interconnection of devices to share data and perform other functions.
Computer networking involves the linking of different computer devices (known as hosts) by others and interfaces designed to ensure effective connection, security, and sometimes, integrity.
To proceed, it is pivotal for us to understand that a network essentially is, at its most basic level, a combination of elements that make up a system. Now, let's take a look at those elements.

An Introduction to Basic Networking Concepts and Principles
Also Read: Network Address Translation(NAT): A Useful Tool for IPV4 Address Translation
A simple computer network usually has components that are linked together to carry out operations. These components are broadly divided into three classes:-
a) The host devices: It is also known as end devices, are the components of the network that most people interface with, they are usually the source and final destination of networking information. Host devices include computers, phones etc.
A network could consist of numerous end devices, so, to distinguish them and ensure proper information routing, a networking principle known as IP (internet protocol) addressing is used.
The host devices are assigned unique numbers to identify them as part of a network. Currently, there are two versions of IP addresses:-
- Internet protocol version 4 (IPv4)
- Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6 )
b) The intermediary/networking devices: These devices are the links between host devices and the network or they can connect different networks together in an internetwork. Their primary function includes:-
- Linking end devices
- Routing data from one end device or network to another by regeneration and retransmission of signals.
- Ensuring security and fast delivery etc.
- Maintaining path information and communicating failure in links.
Examples of intermediary devices include routers and switches. Routers are devices whose primary function involves linking multiple networks and routing data through them. A switch on the other hand links different host devices in one network.
c) The network media: It is basically the channel through which signals pass from a source to a destination in the network. They include :-
- Metallic wires
- Fiber optics
- Wireless transmitters.
Now that we have treated the fundamental components of a typical network it's important to look at what kind of networks are out there.
What are the types of Networks
Networks can be classified based on many factors. But there are two popular ways to look at them.
A) Classification based on Area
If we decide to consider networks based on the area they cover then some of the common types includes below.
a) Local Area Networks (LAN ): this is one of the simplest forms of networks, this network typically includes a few network devices in a small geographical area. For instance, the network in a corporate office building is a LAN. WLAN (wireless LAN) is a popular type of LAN where communication between the devices is through wireless media.
b) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): as you can deduce from the name, MANs are networks covering a city-wide range. They are normally owned by governments.
c) Wide Area Network (WAN): this is a type of network that covers a wider geographical area than a MAN. The geographical area might be as wide as even continents. The most popular example of these WANs is the internet.
d) Virtual Private Network (VPN): this is a point-to-point connection between two host devices through an encrypted channel. VPNs are normally used to ensure secure communication.
B) Classification based on Physical Topology
Networks can also be classified based on how the devices in the network are arranged and the physical connections. Considering these criteria, four common types of network topologies includes below.
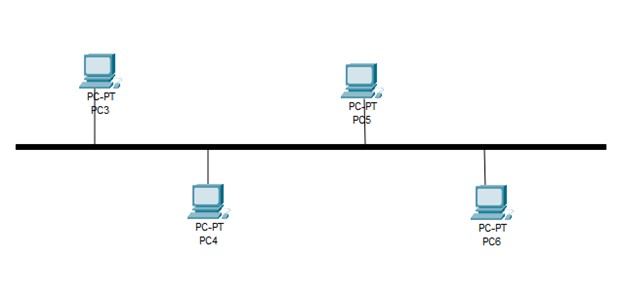
a) Bus network topology: This is the most often used topology in LANs. In this architecture, the host devices (nodes) are all connected to a main cable, sometimes referred to as a bus. The main advantage of using this topology is that it is very easy to install and extend. Along with that it is also very cost effective. But if you are looking for speed, performance, reliability, or number of supported nodes then perhaps you should consider using any other network topology.
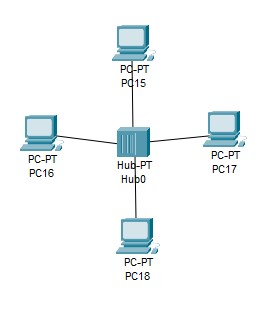
b) Star network topology: In this setup, all the nodes are connected to a single point (usually a hub) at the center. It can be divided into a logical star topology or a physical star topology. In a physical star topology, central hub or a bridge controls the communications to and from attached nodes.
The main advantage of using star topology is that it is very easy to troubleshoot and provide better performance. But if you are looking for a complex system where you don't want to be too much dependent on central bridge then perhaps you should consider some other network design.
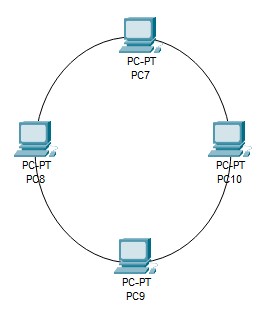
c) Ring network topology: This network topology involves connecting nodes in a loop. Each of them is made to have a single neighbor on each side. In the ring network topology, a frame is passed from node to node until it reaches its destination. This topology is mostly used for Token Ring and FDDI LANs.
The main advantage of using ring topology is that there is no need to have a mechanism to ensure collision-free datagram passing. It can also be extended to cover greater number of nodes and is fairly simple to maintain. But at the same time any one node failure on the ring can cause an outage to all connected nodes.
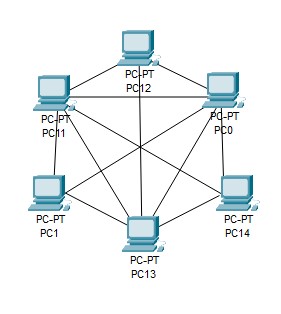
d) Mesh network topology: In this network topology, each and every node in network is connected to each other. This is a network topology that ensures high redundancy by connecting nodes in an overlapping manner. This topology is mostly preferred for Wireless networks. Mesh network topology is further divided into full mesh and partially connected mesh topology.
The main advantage of using this network topology is that it can handle large amount of traffic and any failure of one node does not break the entire node on the network. But at the same time it is very costly to implement as compared to other network topologies.
 Aside a physical topology, networks also have a logical topology. This refers to the logical configurations behind the physical implementation of the network. The logical topology considers things like the naming convention of the devices, the IP addressing scheme etc. Usually, the logical topology is first designed and then implemented as a physical topology.
Aside a physical topology, networks also have a logical topology. This refers to the logical configurations behind the physical implementation of the network. The logical topology considers things like the naming convention of the devices, the IP addressing scheme etc. Usually, the logical topology is first designed and then implemented as a physical topology.
Network Protocols and Layers
Network protocols and network layers are two very important aspects of the topic. Let's take a look at them.
a) Network Protocols
Networking protocols refer to a set of standards and principles governing the transmission of data from one device to another in a network. These protocols are fundamental to how the devices in the network interface with each other - how they communicate.
As you must have already noticed, networks are usually made up of different devices with different designs and underlying infrastructure. The protocols are the rules that govern how these devices work together. Without the network protocols, communicating with each other would be almost impossible for the devices.
There are several protocols and different organizations backing them. For example IEEE, ISO, and ITU have their sets of network protocols or standards. But all protocols fall under one of 4 classifications :-
- Communication protocols are the protocols that are primarily concerned with communication between network devices. For eg: Internet Protocol (IP), Bluetooth transfer protocol, and instant messaging protocols.
- Security protocols are a set of protocols that ensure the security of the data sent over networks and the networks themselves. For eg: Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols and encryption protocols.
- Routing protocols govern the operation of routers. It enables them to exchange information about routes, compare data, and select the best route to a destination. For eg: OSPF (open shortest path first) and BGP (Border gateway protocol).
- Service discovery protocols aid the automatic detection of devices, connections, or services. For eg: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS).
b) Network Layers
From picking up data from the source to interpreting it at the destination, a network is implemented in functional layers. At each layer, information passes through additional processing, is encoded (based on the protocols in that layer), and moved to the next layer. This continues until it gets to the destination where it is decoded. The protocols discussed earlier all fall under certain layers.
Therefore, a network can be divided into layers - conceptual models. The most popular models for classifying network layers include the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) model.
Let's take a look at the seven layers in the OSI model and the protocols that exist in them:-
- The physical layer is at the bottom of the OSI model, this layer is concerned with transmitting and receiving unstructured raw bit streams over a physical medium. Protocols here include USB physical layer and integrated services digital network (ISDN).
- The data link layer ensures the error-free transfer of data frames from one node to another over the physical layer. Protocols here include Ethernet, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) etc.
- The network layer controls the operation of the subnetworks, mostly concerned with routing. Protocols here include Internet Protocol (IP), Open shortest path first (OSPF) etc.
- The transport layer ensures ordered and loss-free delivery of messages. Protocols here include Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User datagram protocol (UDP).
- The session layer establishes sessions between processes. Protocols here include Server Message Block (SMB), Short Message Peer-to-Peer (SMPP) etc.
- The presentation layer formats the data to be presented to the application layer. It functions as a translator for the network. Protocols here include Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Socket Tunneling (SSL).
- The application layer is the medium through which users and app processes access network services. Protocols here include Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) and Domain Name System (DNS).
These layers all work together to ensure the network as a system successfully carries out its operations.
Wireless Networks
Over the years network technologies has taken a strong leap forward resulted in the development of Wireless Networks which is probably the most used networks today. Today in almost every famous electronic devices, you would find a wireless adapter in it to connect to the wireless networks. As more and more network devices developed, there are certain common standards also developed which every manufacturer needs to adhere to. We will see some of the famous standards below. But before that let's understand few of the basic concepts in Wireless networks.
a) CSMA/CA
CSMA/CA, also known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance is an access method used in Wireless networks. Every wireless devices in a network uses this access method to get the hold of access point to transfer the data packets.
b) Radio Waves
As the name suggests, radio waves are the waves in radio frequency zone of the electromagnetic spectrum. All wireless communications goes through the radio waves. The basic principle of generating radio waves is by through passing an alternating current through a conductor and transmitted out from an antenna.
c) Frequency
Frequency is defined as the number of cycles it takes to complete per second. Each cycle is measured in a unit called Hertz(Hz). Every radio wave has some frequency. The higher the frequency, the shorter is the wavelength. However higher frequency facilitates more data transfer per second.
d) Modulation
Modulation is a method of modifying the amplitude, frequency or phase of transmitting radio waves to increase the efficiency. There are many different types of modulation techniques which can be efficiently utilizes in multiple frequency bands to provide the best usage of available bandwidth. We will see few of the modulation techniques used in different wireless standards in below section.
e) IEEE 802.11a
The IEEE 802.11a is a wireless standard supported for devices using 5 GHz frequency range. It was developed way back in September 1999. 802.11a utilizes Orthogonal Frequency Distribution Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation technique to provide the best usage of available bandwidth.
f) IEEE 802.11b
The IEEE 802.11b is a wireless standard supported for devices using 2.4 GHz frequency range. It was also released along with IEEE 802.11a in September 1999. This standard utilizes a modulation technique called Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) to provide efficient use of the available bandwidth.
g) IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11g standard was developed to enhance the capability of IEEE 802.11a. This was released in the year 2003 and provide speed up to 54 Mbps in a frequency band of 2.4 GHz. The IEEE 802.11g standard uses modified OFDM modulation technique to provide the efficient use of available bandwidth.
h) IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11n supported both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, therefore devices utilizing both the frequency band are called dual-band. The devices supporting this standard usually has multiple antennas and utilizes the concept of Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) antennas.
i) IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ac uses single 5 GHz frequency band. This is a very recent standard which uses a very efficient modulation technique called Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) to utilize the available bandwidth. The improvements added in this standard resulted in overall speed of 1.3 Gbps which is much more than the previous achieved speed in other standards.
Conclusion
Networks consist of components that communicate to ensure data is passed from a point to another. You can conceptually view networks as existing in functional layers with rules governing the operation at each one. In this article, we have seen about different types of networks. We have also gone through the basic understanding of Network protocol and layers. At last, we have gone through brief introduction of Wireless networks and some of its famous standards used.
